1. Introduction
With the rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision Language Models (VLMs), AI technology is shifting from exam-oriented task completion to practical scenario-based complex problem-solving. Using LLMs and VLMs to tackle more realistic and intricate problems—rather than simply passing exams—is not only an inevitable direction of technological evolution but also a key requirement for industrial applications. Meanwhile, the wave of AI agents driven by LLMs continues to expand AI’s application boundaries in the physical world: from GUI-based online shopping operations to physically embodied robots performing household chores. Enabling agents to perceive environments, plan, make decisions, and interact like humans has become a shared challenge for academia and industry.
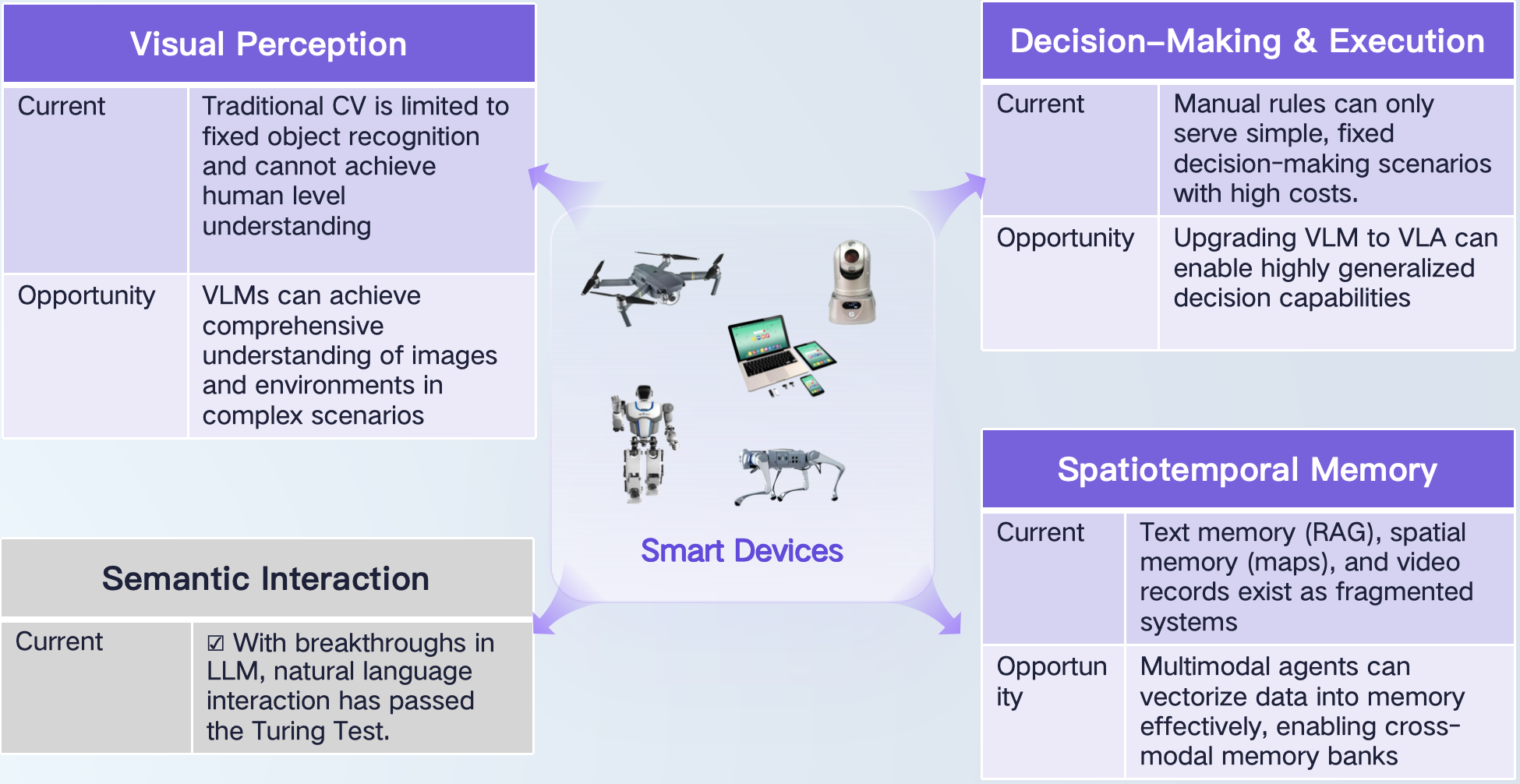
What users truly need are general-purpose agents capable of delivering results and completing tangible tasks in the physical world. Guided by this goal, we focus on exploring a practical technical roadmap: building AI agents that can solve various problems in the physical world, deployable on devices as the core brain component. In the future, devices such as smartphones, cameras, robots, and drones are expected to become embodied AI agents, and be applied to diverse fields like industrial management, medical diagnosis, personal assistance, and media creation. To realize such embodied AI agents, four core capabilities must be achieved: visual perception, decision-making & execution, semantic interaction, and spatiotemporal memory. Among these, semantic interaction has been initially addressed by current LLMs, and the other three remain as challenges and opportunities for technological innovation. In February of this year, we released the reinforcement learning-driven VLM-R1 model and received widespread attention. By extending DeepSeek’s reasoning capabilities from natural language to vision-language scenarios, we validated the effectiveness of using reinforcement learning to enhance VLM’s visual perception and complex environmental reasoning abilities. Recently, we further expanded this to the field of decision-making & execution and, combined with a multimodal agent framework, launched the first embodied AI agent—OmAgent, a reinforcement learning-based multimodal agent framework. Its feasibility has been verified in practical applications.
2. Method
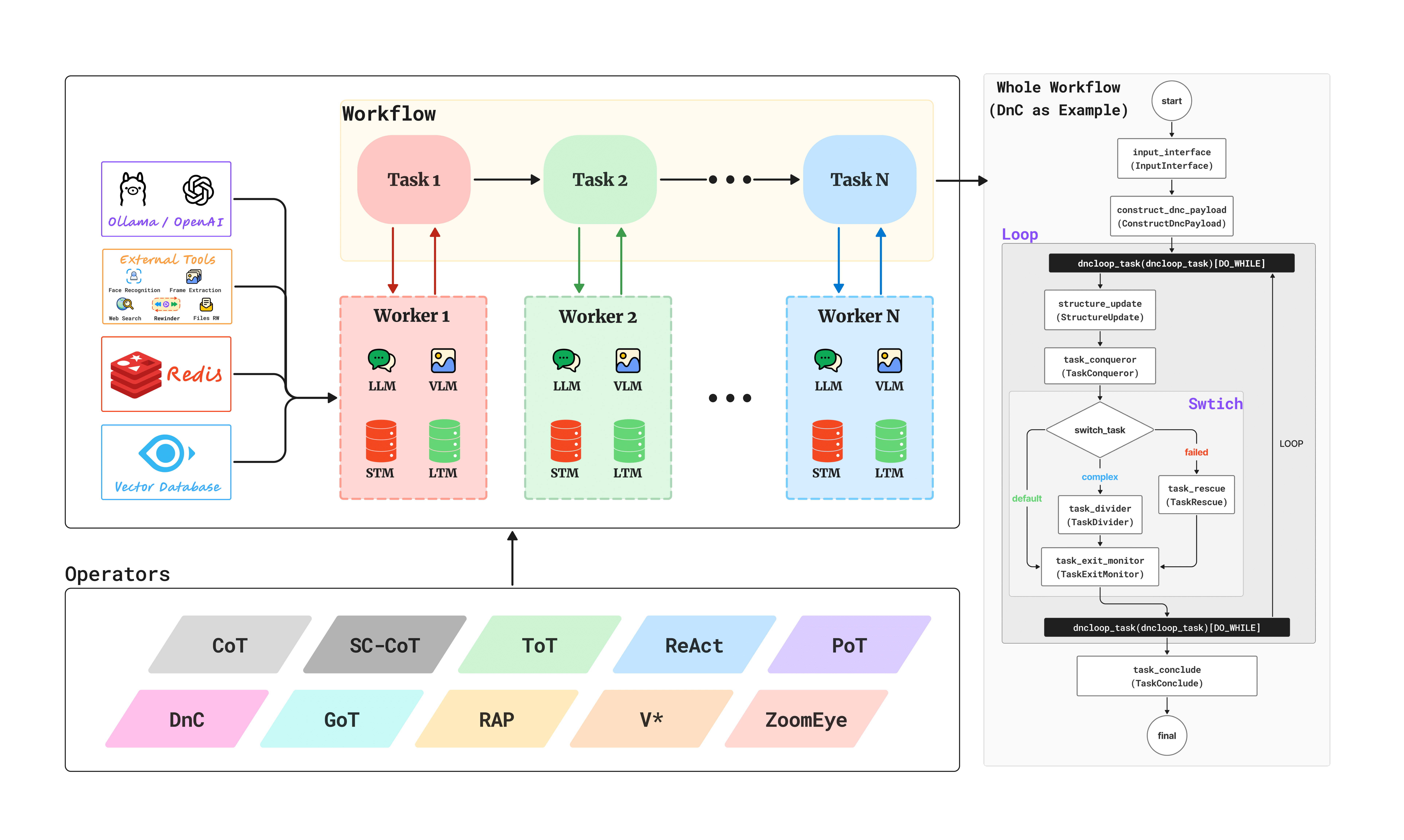
OmAgent is a reinforcement learning-based multimodal agent framework. The core philosophy of this framework is simplifying complexity through abstraction. It encapsulates complex engineering implementations (such as spatiotemporal memory management, workflow orchestration, task queues, and node optimization) in the background, providing developers with a highly streamlined and user-friendly Python interface. It features the following characteristics:
Native Multimodal Support
- VLM Model Integration: Built-in support for mainstream VLMs, including Qwen2.5-VL, LLaVA, InternVL, etc.
- Video Processing Capability: Natively supports video input and processing for video understanding and analysis.
- Mobile Device Connectivity: Enables seamless integration with mobile devices for cross-platform agent deployment.
Reusable Component Abstraction
- Modular Design: Develop complex agents using basic components to improve development efficiency.
- Component Library Ecosystem: A rich set of pre-built components covering common AI task scenarios.
- Custom Extensibility: Flexible extension mechanisms supporting developer-defined components.
Zero-Complexity Development Experience
- Concise API Design: Avoids the heavy developing overhead.
- Automated Engineering: Automatically handles complex engineering implementation details in the background.
- Rapid Prototyping: Transforms ideas into prototypes with just a few lines of code.
OmAgent serves as a core component for smart devices. With multimodal support and zero-complexity development, it can be easily applied to various devices. Additionally, built-in basic algorithm modules and toolkits enable rapid resolution of challenges related to environmental perception, interaction, decision-making & execution, and memory storage. To meet the requirements for visual perception and decision-making capabilities, we integrate reinforcement learning models into OmAgent, enabling devices to maintain robust environmental perception and effective decision-making in dynamically complex environments.
2.1 Breaking Through Visual Perception Capabilities – Reinforcement Learning-Driven Advanced Environmental Perception
Our technical expertise in visual perception dates back to the release of the OmDet model series in 2021. Through multiple iterations, the model evolved from early attribute and relation-based general perception and detection capabilities to an efficient recognition mode driven by natural language instructions. Combined with lightweight training and deployment solutions, OmDet achieves open-domain detection and understanding of the surrounding environment. In 2023, we launched OmChat, continuously enhancing its perception and interaction capabilities in vision-language hybrid environments. In early 2025, leveraging technical breakthroughs from DeepSeek, we successfully introduced reinforcement learning into VLMs, and released the VLM-R1. VLM-R1 significantly outperforms traditional supervised learning methods in various visual perception tasks such as object detection, marking a similar aha moment of cognitive breakthrough in the visual domain. Notably, through training and validation across multiple tasks, our reinforcement learning-based OmR1 model demonstrates excellent generalization in cross-task scenarios, providing flexible technical support for visual perception and decision-making in complex environments.
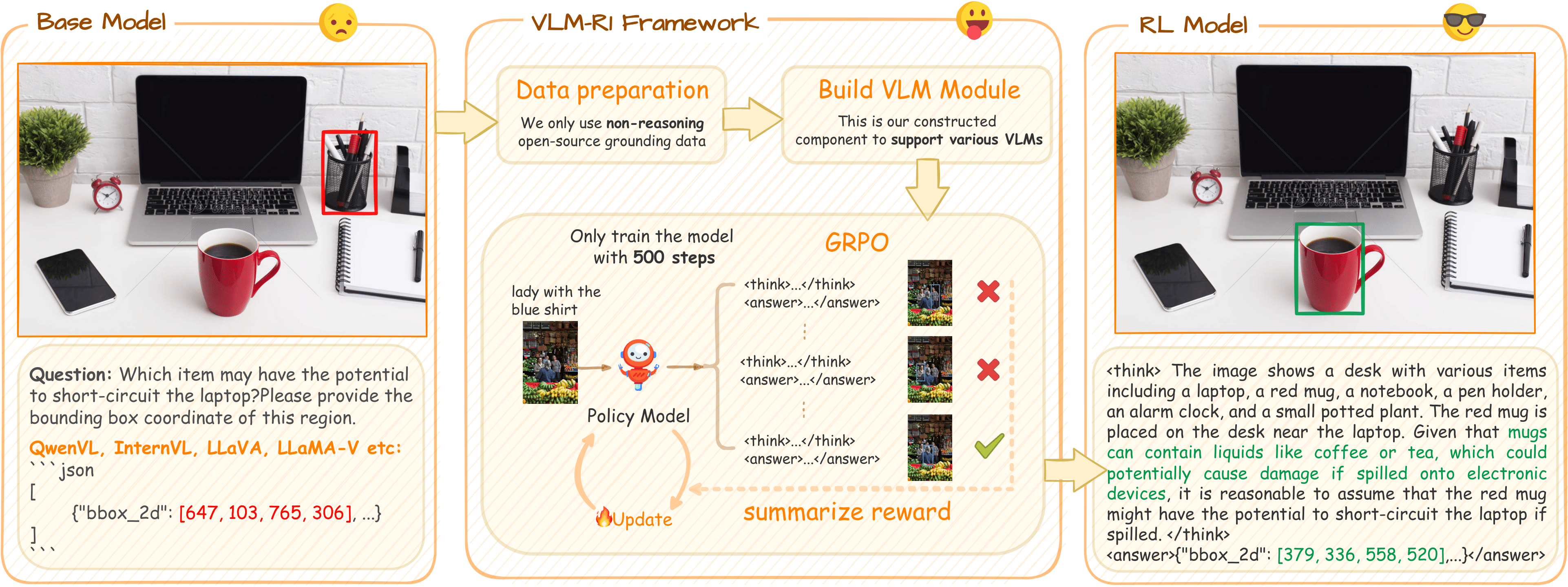
VLM-R1 core technical innovations include:
- GRPO Algorithm Integration:
- Comprehensive integration: Full support for the GRPO algorithm in VLM models.
- Hyperparameter control: Easy control over all training hyperparameters.
- Stable training: Achieves stable RL training through predefined and customized reward design.
- Model compatibility: Supports training of VLM models of different scales, from 3B to 72B models.
- Parameter-Efficient Training:
- LoRA technology: Supports LoRA-based efficient training, which is suitable to resource-constrained cases.
- Multi-node training: Enables distributed training across multiple GPUs or server nodes.
- Efficient training: Optimizes memory usage and training speed.
- Multimodal Data Processing:
- Multimodal training: Supports simultaneous training on image-text and pure text datasets.
- Dynamic batching: Batch processing strategies to improve training efficiency.
- Multi-Task Support:
- REC tasks: Specialized reward design for Referring Expression Comprehension tasks.
- OVD tasks: We also defined the reward function for Open-Vocabulary Detection tasks.
- Extensibility: Supports custom reward functions for different tasks.
In our research, we observed the emergence of "OD aha moment" in VLMs—an intelligent behavior spontaneously developed during reinforcement learning training:
- Internal validation mechanism: The model conducts internal thinking and validation before outputting detection results.
- Two-step reasoning process: The model emergently exhibits to first filter irrelevant objects and then perform precise object detection.
2.2 Embodied Intelligent Decision-Making & Execution – Simulating Human-Environment Interaction
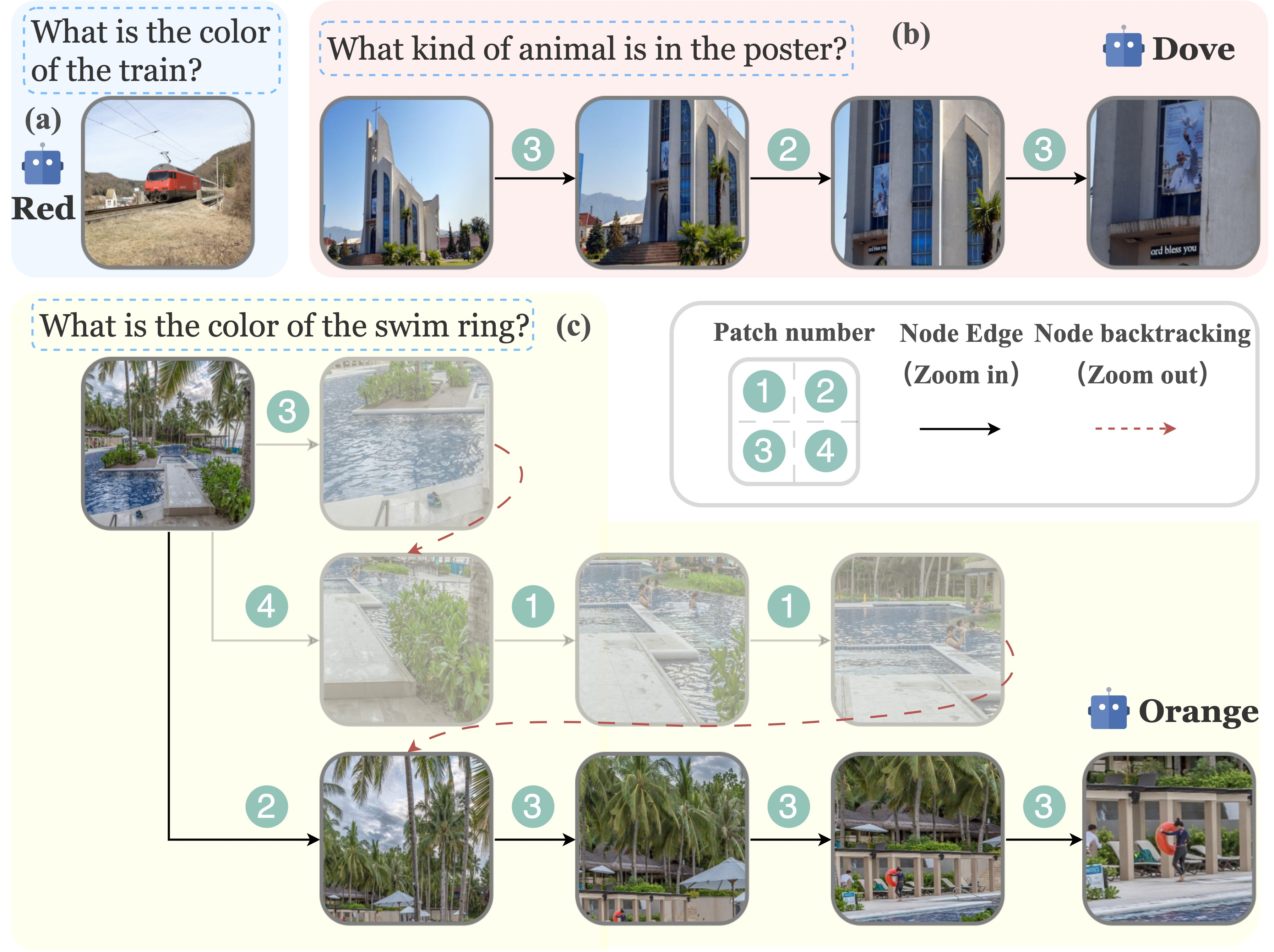
Autonomous decision-making and execution based on environmental perception are the second major challenge in embodied intelligence. In the OmAgent framework, besides relying on VLM models for task decomposition, planning, and calling basic capabilities like MCP, we further simulate the logic of human interaction with the external environment and innovatively propose the ZoomEye algorithm—designed to enhance VLM’s interaction capabilities in high-resolution environments. Its core idea is to replicate humans’ zooming behavior when observing environments: just as human eyes first scan the overall scene and then focus on details, the model can progressively explore and deeply analyze key information in the environment through similar step-by-step exploration. Its core innovations include:
- Tree-Structured Image Processing:
- Hierarchical image modeling: Represents images as a tree structure, where the root node denotes the entire image, and child nodes represent zoomed sub-regions of parent nodes.
- Recursive segmentation strategy: Recursively splits images into four equally sized sub-regions based on preset resolution constraints.
- Depth control mechanism: Controls zoom levels through node depth, enabling progressive exploration from global to local.
- Error recovery mechanism: Equipped with capabilities to handle recovery from search failures.
- Human Vision Simulation:
- Zooming behavior simulation: Simulates the zoom-in and zoom-out operations in human visual observation.
- Attention guidance: Guides the search process based on visual cues, focusing on relevant regions.
- Backtracking mechanism: Supports returning to the previous view from the current view to explore other regions of interest.
- Resolution adaptation: Automatically adapts to images with different input resolutions.
- Confidence Evaluation System:
- Existing Confidence: Evaluates the probability of the target object existing in the current view.
- Latent Confidence: Assesses the possibility of discovering the target object through further zooming.
- Answering Confidence: Evaluates whether current visual information is sufficient to answer the question.
3. Performance Evaluation of OmAgent in Industrial Applications
To verify the practical performance of OmAgent, we conducted comparative tests between OmAgent and mainstream VLMs on three industrial scenarios—open detection, visual cognition (complex event detection), and doc parsing (complex multimedia document understanding)—using a hardware environment equipped with 8 × 80G A100 GPUs.
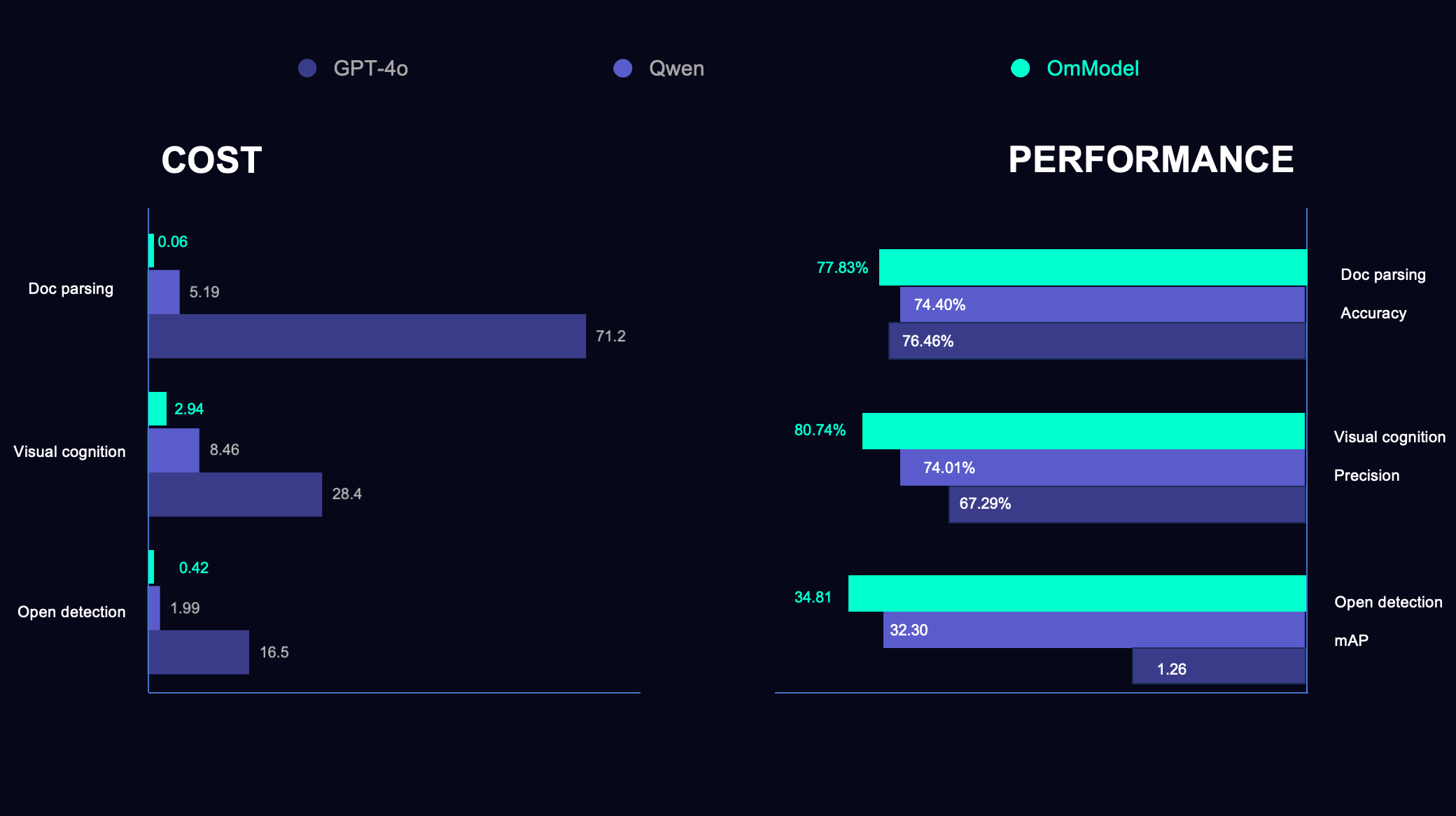
Open Detection Scenario
| Model | Vendor | mAP | Latency (s/frame) | QPS | Cost (RMB/1000 frames) | Avg Output Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OmDet (1B) | Om AI | 30.80 | 0.01 | 800 | 0.02 | - |
| OmR1 (3B) | Om AI | 34.81 | 1.51 | 45.73 | 0.42 | 149.25 |
| GPT-4o | OpenAI | 1.26 | 2.73 | 4.81 | 16.5 | 58.67 |
| Qwen2.5VL-32B | Alibaba | 32.30 | 3.31 | 9.68 | 1.99 | 127.39 |
In the performance evaluation of open detection tasks, we used OVDEval as the evaluation dataset, which covers diverse general detection capabilities in open scenarios, including object attributes, small objects, and non-existent objects. First, as our ultra-lightweight solution, OmDet achieves an excellent 30.80 mAP with only 1B parameters, while achieving a latency of 0.01 seconds and QPS up to 800, providing an efficient solution for real-time scenarios. By introducing reinforcement learning into VLM models, OmR1 can recognize more complex objects and categories through reasoning, reaching 34.81 mAP—significantly outperforming other models and verifying the potential of reinforcement learning in VLMs. Another notable achievement is our breakthrough in cost control: OmDet’s processing cost is only 0.02 yuan per 1000 frames, 825 times lower than that of GPT-4o. OmR1 with a 3B model size, is 38 times lower in cost compared to GPT-4o.
Complex Event Judgment
| Model | Vendor | Precision | Latency (s/frame) | QPS | Cost (RMB/1000 frames) | Avg Output Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OmR1 (3B) | Om AI | 80.74% | 3.02 | 6.56 | 2.94 | 174.45 |
| Qwen2.5VL-32B | Alibaba | 74.01% | 3.77 | 2.08 | 8.46 | 31.38 |
| GPT-4o | OpenAI | 67.29% | 4.68 | 4.09 | 28.4 | 32.68 |
Visual cognition (complex event detection) is a general judgment model for surveillance scenarios, focusing on intelligent analysis tasks across different environments. In this task, users can customize complex management rules for different cases and flexibly define complex abnormal events through instructions. The built-in model agent should conduct environment understanding, anomaly analysis, and accurately mark abnormal areas in images based on these definitions. In this industrial application, the reinforcement learning-based OmR1 model also performs excellently. OmR1 achieves 80.74% precision, significantly outperforming other larger models. Through reasoning, OmR1 outputs an average of 174.45 tokens, enabling more detailed and in-depth analysis in complex reasoning processes. From a cost-effectiveness perspective, OmR1 reduces processing costs by nearly 90% compared to GPT-4o, demonstrating strong practical value in real-world applications.
Complex Multimedia Document Understanding
| Model | Vendor | Accuracy | Latency (s/page) | QPS | Cost (RMB/1000 pages) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OmDoc (1B) | Om AI | 77.83% | 0.27 | 299.2 | 0.06 |
| Qwen2.5VL-32B | Alibaba | 74.40% | 4.56 | 3.71 | 5.19 |
| GPT-4o | OpenAI | 76.46% | 8.16 | 0.836 | 71.2 |
Doc parsing (complex multimedia document understanding) tasks focus on parsing, memory storage, and question answering for long documents with complex structural relationships, including tables, figures and charts. OmDoc, our document agent application, demonstrates significant technical advantages. In terms of performance, OmDoc achieves 77.83% accuracy, outperforming other larger models, while maintaining high precision and leading performance across the board. In terms of efficiency, OmDoc controls processing latency to 0.27 seconds, 17 times faster than Qwen2.5VL-32B and 30 times faster than GPT-4o. This millisecond-level response speed provides a solid technical foundation for real-time document analysis applications. In terms of throughput performance, OmDoc reaches a QPS of 299.2, offering strong technical support for large-scale batch processing scenarios. Most notably, OmDoc excels in cost control, with a processing cost of only 0.06 yuan per 1000 pages—1187 times lower than GPT-4o’s 71.2 yuan per 1000 pages.
4. Open-Source Contributions
We have fully opened our core technology system to the open-source community, receiving enthusiastic responses with over 9K stars accumulated on GitHub:
- VLM-R1 Reinforcement Learning Framework: https://github.com/om-ai-lab/VLM-R1
- ZoomEye Tree Search Algorithm: https://github.com/om-ai-lab/ZoomEye
- OmAgent Multimodal Agent Framework: https://github.com/om-ai-lab/OmAgent
- OmDet Open Visual Perception: https://github.com/om-ai-lab/OmDet
- OmChat Vision-Language Interaction: https://github.com/om-ai-lab/OmChat
5. Future Directions
The evolution of smart devices is never straightforward and a single model cannot solve; it must balance environmental complexity, task diversity, and interaction relevance. Our vision is to inject a complete intelligent persona into every future smart device, with OmAgent as the technical core. We look forward to seeing all devices in the physical world break through their current functional boundaries, transforming into embodied agents capable of autonomous perception, proactive decision-making, and continuous evolution. Let agents play a vital role in various fields such as industrial safety management and medical diagnosis, enabling AI to step out of data centers, deeply integrate into the physical world, and become a core driver of industrial upgrading and life transformation.
For more technical details and open-source projects, please visit: Om AI Lab GitHub
For technical exchanges and cooperation, please contact us.